Roof insulation materials comparison sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Exploring the various types, installation methods, environmental impact, and cost comparisons of roof insulation materials provides a well-rounded view of this crucial aspect of building efficiency and sustainability.
Types of Roof Insulation Materials
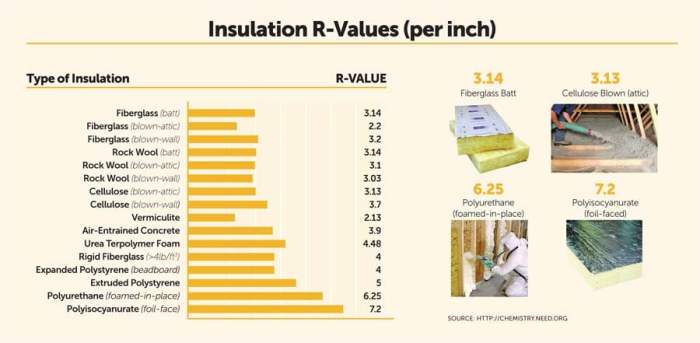
When it comes to roof insulation materials, there are several options available, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. One of the key factors to consider when choosing insulation is the R-value, which measures the material's thermal resistance.Fiberglass insulation is a popular choice for roofs due to its affordability and effectiveness.
However, it has a lower R-value compared to other materials, meaning it may not provide as much insulation in colder climates.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fiberglass Insulation
- Advantages:
- Affordable
- Easy to install
- Effective at reducing heat transfer
- Disadvantages:
- Lower R-value than other materials
- Can irritate skin and lungs if not handled properly
- Prone to moisture absorption
Differences between Foam Board Insulation and Spray Foam Insulation
Foam board insulation and spray foam insulation are two popular options for roofs, each with its own unique characteristics.
- Foam Board Insulation:
- Rigid panels made of polystyrene, polyurethane, or other materials
- Higher R-value compared to fiberglass insulation
- Can be more expensive but offers better insulation properties
- Spray Foam Insulation:
- Applied as a liquid that expands and hardens into a foam
- Provides a seamless air barrier when properly installed
- Higher R-value than foam board insulation
Installation Methods
When it comes to roof insulation, the installation method plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness and efficiency of the insulation. Different types of roof insulation materials require specific installation methods tailored to their properties and benefits. Let's explore the installation methods for reflective insulation, cellulose insulation, batt insulation, and blown-in insulation.
Reflective Insulation Installation
Reflective insulation is typically installed in the roof by stapling it to the underside of the roof rafters or trusses. The installation process involves unfolding the reflective insulation material and securing it in place with staples. It is important to ensure that there are no gaps or overlaps in the material to maximize its reflective properties.
Additionally, a vapor barrier may be required to prevent moisture buildup in the roof.
Cellulose Insulation Installation
Installing cellulose insulation in an attic space involves blowing or spraying the cellulose material onto the attic floor or between the roof rafters. The process requires specialized equipment to evenly distribute the insulation material and achieve the desired R-value. It is important to fill all gaps and voids in the attic space to prevent heat loss and improve energy efficiency.
Batt Insulation vs. Blown-in Insulation Installation
Batt insulation, such as fiberglass or mineral wool, is typically installed in the roof by placing pre-cut batts between the roof rafters or trusses. The installation process involves measuring and cutting the batts to fit the space and securing them in place with staples or clips.
On the other hand, blown-in insulation, such as cellulose or fiberglass, is installed by blowing or spraying the insulation material into the roof cavity using specialized equipment. Blown-in insulation is more suitable for hard-to-reach areas and irregular spaces, providing better coverage and energy efficiency compared to batt insulation
Environmental Impact
Recycled denim insulation has gained popularity due to its eco-friendliness. By repurposing old denim jeans into insulation material, this option helps reduce waste in landfills and minimizes the need for new raw materials. This process also saves energy compared to producing new synthetic insulation materials, making it a more sustainable choice for roof insulation.
Eco-Friendliness of Recycled Denim Insulation
Recycled denim insulation offers a significant environmental benefit by diverting waste from landfills and reducing the energy required for production. The denim fibers provide effective insulation while being non-toxic and safe to handle during installation. Additionally, the insulation can be recycled again at the end of its lifespan, further contributing to sustainability efforts.
Sustainability of Natural Wool Insulation
Natural wool insulation is derived from sheep's wool, making it a renewable and biodegradable material. Compared to synthetic insulation materials that are petroleum-based, natural wool has a lower carbon footprint and requires less energy to produce. Wool insulation also has the ability to regulate moisture levels and absorb harmful chemicals from the air, creating a healthier indoor environment.
Impact of Roof Insulation on Energy Efficiency
The choice of roof insulation material can greatly impact the energy efficiency of a building. Proper insulation helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems to run continuously. By using sustainable and energy-efficient insulation materials like recycled denim or natural wool, buildings can lower their energy consumption and carbon emissions, contributing to a greener environment.
Cost Comparison
When comparing different types of roof insulation materials, cost is a crucial factor to consider. The initial investment and long-term expenses can vary significantly depending on the material used.Rigid foam insulation is generally more expensive upfront compared to mineral wool insulation.
However, rigid foam insulation offers higher R-values, which means better insulation and energy efficiency for your home. This can result in lower heating and cooling costs over time, potentially offsetting the initial investment.On the other hand, mineral wool insulation is more cost-effective initially but may not provide the same level of insulation as rigid foam.
This could lead to higher energy bills in the long run, negating the cost-saving benefits of the lower initial investment.
Long-Term Cost Benefits
- High-quality roof insulation materials like rigid foam offer better insulation, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills in the long run.
- Investing in high-quality insulation upfront can result in significant cost savings over the lifespan of your roof.
- Proper insulation can also extend the lifespan of your roof by preventing moisture buildup and reducing the risk of damage, saving you money on repairs and replacements.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of roof insulation materials comparison is key to making informed decisions for your building. Whether considering environmental impact, cost efficiency, or installation ease, this guide has shed light on the essential factors to consider.
Essential FAQs
What is the R-value and why is it important in roof insulation materials comparison?
The R-value measures the insulation material's resistance to heat flow. A higher R-value indicates better insulation performance.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using fiberglass insulation for roofs?
Fiberglass insulation is cost-effective and easy to install but may cause skin irritation during handling.
How does the choice of roof insulation material impact energy efficiency in a building?
The right insulation material can reduce heat loss and gain, leading to lower energy consumption for heating and cooling.










